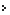Latitude:
30°22'40" N to 33°12'40" N
Latitude:
30°22'40" N to 33°12'40" NLongitude: 75°45' 55" E to 79°04' 20" E
Himachal Pradesh, as the name suggests, is situated in the western Himalayas. It extends from the latitudes 30°22'40" North to 33°12'40" North and longitudes 75°45' 55" East to 79°04' 20" East. Located in the northern part of India, the state stands bordered by Punjab in the west, Uttar Pradesh in the southeast, China in the east, Haryana in the southeast and Jammu and Kashmir in the north. The entire state of Himachal has a hilly and rugged terrain, with the altitude ranging from 350 meters to 7000 meters above sea level.
In fact, the average altitude of the state increases as we move from west to east and from south to north. In geographical terms, we can divide the entire state of Himachal Pradesh into three distinct regions, namely the Shivalik or Outer Himalayas, Middle Himalayas or Inner Himalayas and Greater Himalayas or the Alpine Zone. The Outer Himalayas cover the altitude ranging from 350 to 1,500 meters. They comprise of the districts of Hamirpur, Kangra, Una, Bilaspur, and the lower parts of Solan, Sirmaur and Mandi.
Talking about the Middle Himalayas, one has to mention that they cover the altitudes ranging from 1,500 to 4,500 meters. The districts Sirmaur, Mandi, and the upper parts of Kangra, Shimla and Chamba make up this region of Himalayas. Finally, we come to the Greater Himalayas that comprises of all those areas which exceed 4,500 meters in altitude. To be more precise, this region includes Sutlej River, apart from the Kinnaur and Pangi tehsils of Chamba and some parts of Lahaul and Spiti, within its precincts.