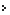Geographical Area: 51,125 km (93% is mountainous and 64% is covered by Forest)
Geographical Area: 51,125 km (93% is mountainous and 64% is covered by Forest)Uttarakhand is situated on the southern slope of the mighty Himalayas. The climate and vegetation of different cities of this state vary with the altitude of its location. Glaciers being located at the highest elevations have coolest weather and are covered by ice and bare rock. However there is dense tropical forest at the lower elevations. The Western Himalayas between 3000-3500 meters are covered with Alpine Shrub and Meadows. Two of India's mightiest rivers, the Ganges and the Yamuna start off from the glaciers of Uttarakhand. There are also several other perennial lakes and many streams in the region. The geography of Uttarakhand is so much varied that it has been geographically divided into two parts, the western half known as Garhwal and the eastern region as Kumaon.
Uttarakhand- Climate
The climate of Uttarakhand is stridently distinguished in its two diverse divisions: the major hilly terrain and the smaller plains. The northern part of the state enveloped in the mighty Himalayas shows complete traits of Himalayan climate exerting an appreciable extent of influence on monsoon and rainfall patterns. The climate however also varies within the mountains in accordance with the altitude of the place. In the southern foothills, the average summer temperatures vary between 30°C to 18°C and winter is also bearable and normal. In the areas of the Middle Himalayas, the summer temperatures are usually around 15 to 18°C; however winters temperature even drop below the freezing point. The higher altitudes of Himalayas (more than 15,000 feet) are cold throughout the year and at times become inaccessible due to heavy snowfall. The eastern edges of the Himalayan ranges are subject to heavy rainfall while the western division is relatively dry. However in Gangetic plains, summers are extremely hot and humid with temperature crossing the 40°C mark. Winters here can be relatively quite cold with temperatures dipping below 5°C at times.
Uttarakhand- Topography
Topography of Uttarakhand involves the terrain and the landforms existing within its provinces. Set amidst the mighty Himalayas, the topography of Uttarakhand has a distinct range of landforms varying from hills and peaks to cliffs and crests. There are several varieties of rich forests, many glaciers, mountains, rivers and perennial lakes in this state.
- Major peaks- Nanda Devi, Mount Kamet , Abi Gamen , Mukut Parvat , Chaukhamba, Trishul, Kedarnath, Neelkanth, Shivling, Nilgiri and Bandarpoonch
- Major Rivers- Ganga, Yamuna, Bhagirathi, Alakananda, Kosi, Mandakini, Pindar and Saryu
- Major Glaciers- Maiktoli Glacier, Kaphini Glacier, Ralam Glacier,, Sunderdhunga Glacier, Chorbani Glacier, Gangotri Glacier, Khatling Glacier and Nandadevi Glacier.
Uttarakhand-Biodiversity
The biodiversity of Uttarakhand is rich due to the sacred groves that exhibit a rich variety of flora and fauna. The area exhibits typical Himalayan variety in its Northern region. However, it also consists of several of rare and threatened species of plants and animals. The Garhwal region is the land of alpine meadows full of numerous varieties of spring flowers. Other than this, the landscape of Uttarakhand also contains a numerous variety of animals. Some of these animals are-Himalayan blue sheep, Musk Deer, Lynx, Snow leopard, Monkeys. Rare varieties of birds like bearded vulture are also seen in this area. From tropical forests to Alpine shrubs and meadows, the flora of Uttarakhand is also varied as per climatic changes due to elevate-changes. Uttarakhand also has rich variety of medicinal plants. The biodiversity of Uttarakhand is, certainly, a delight as it helps the region in maintaining its vivacity.