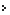Chham dance is splendid dance performed by the
Buddhist monks, known as Lamas, in the courtyard of monasteries during
religious and other festivals, as a part of the celebrations. The dance
is known for the elaborate mask, headgear and costume of the performers
and is very popular in Tibetan settlement areas of Himachal Pradesh,
such as Lahaul & Spiti, Ladakh and Kinnaur. The villagers gather
together to witness this magnificent dance show, also known as the
'Devil Dance'.
It is believed that the Chham dance is performed to exorcise evil
spirits and demons. The theme rotates around killing the 'Evil King',
who is symbolic of evil tendencies in humans, natural calamities,
diseases and epidemics. The oversized masks, with weird expressions and
monstrous appearances, used in the dance are made up of wood, papier-mâché
and thin coat of plaster. They represent the numerous dreadful monsters,
in the form of dragons, devils, evil spirits and skeletons, waiting for
the soul after death.
The movements in Chham Dance are slow and circular and are accompanied
by the beat of drums, cymbals and long pipes. Costumes are often made up
of brocade silk in bright hues of red, blue, yellow, pink and green.
Lamas themselves make the masks, strictly according to the stated rules.
The deities that usually form the characters of this performance include
the God of Wealth and 'Yama' or the God of Death, along with his demons.
Other deities are 'Padmasambhava' or the second Buddha; the Guardian
Angel of Horses and other Animals; and the Great Tempter. Chham Dance is
performed under the supervision of the senior Lamas of a monastery. The
weapon of 'Phurbu' also forms a part of this dance. It is basically a
clover blade with the head of 'Khyunk' (hawk) on its top, believed to be
the magic dagger of tantric deities that they use to subdue demons. The
weapon is generally made of either steel or bronze or wood.